Log-Shipping Replication
Primary 서버에서 만드는 WAL 파일을 정기적으로 Standby 서버로 옮기고, 그것을 적용시켜 Primary 서버가 장애로 멈추기 되면 Standby 서버를 운영하는 방식.
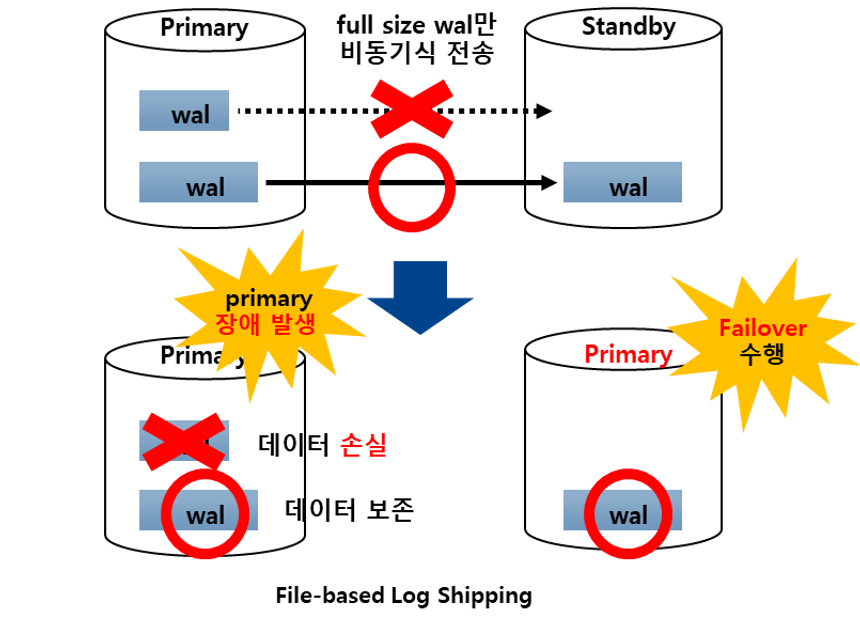
Log-Shipping Replication의 특징
- Primary 서버와 Standby 서버가 모두 실행 중이어야 합니다.
- Primary 서버는 아카이브모드로 운영 되어야 합니다.
- 로그 전달 방식은 비동기식 입니다.
- 전송하는 WAL 파일의 내용은 이미 커밋된 자료이기 때문에, 그 데이터가 Standby 서버로 미쳐 전달 되기전에 Primary 서버가 멈춰버리면 그 데이터는 손실됩니다.
- warm standby 방식이기 때문에 Standby 서버 쪽에서는 어떤 쿼리도 사용할 수 없습니다.
Log-Shipping Replication 구축 방법
Primary 서버 구성
1. Standby 서버에 ssh 패스워드 인증없이 바로 접속할 수 있도록 설정합니다.
ssh-keygen ssh-copy-id -i /home/[Primary USER]/.ssh/id_rsa.pub [Standby USER]@[Standby IP]
2. postgresql.conf 파일을 수정합니다.
`listen_address=’*’
port=5432
wal_level = replica
archive_mode = on
archive_command=’scp -i home/[Primary USER]/id_rsa %p [Standby USER]@[Standby IP]:[archive file Path]/%f
archive_timeout = 30
max_wal_senders=2`
3. pg_hba.conf 파일을 수정합니다.
host replication [DBUSER] [Standby IP/CIDR] trust
Standby 서버 구성
1. pg_basebackup을 이용한 백업을 합니다.
/usr/local/pgsql/bin/pg_basebackup -h [Master IP] -p 5432 -U [USER] -D [DATACLUSTER DIR]
2. recovery.conf를 postgresql.conf 파일과 같은 위치에 생성합니다.
`restore_command = ‘cp [archive file Path]/%f %p’
archive_cleanup_command=’/usr/local/pgsql/bin/pg_archivecleanup [archive file Path/ %r’
standby_mode = ‘on’`
- restore_command : cp나 copy 커맨드를 사용하여 archive로부터 WAL 파일을 복구하기 위해 파일 경로를 작성합니다.
- pg_archivecleanup을 이용하여 archive 경로에 restore된 WAL 세그먼트들을 정리합니다.
3. archive 디렉토리 생성 후 소유권을 변경합니다.
mkdir [Archive file Path] chown [Standby USER] [Archive file Path]
4. Standby 서버를 재기동합니다.
pg_ctl restart
확인
Primary 서버
[tmax@JY2C4G02:data]$ ps -ef | grep postgres
tmax 20465 1 0 11:24 pts/1 00:00:00 /usr/local/pgsql/bin/postgres
tmax 20467 20465 0 11:24 ? 00:00:00 postgres: checkpointer
tmax 20468 20465 0 11:24 ? 00:00:00 postgres: background writer
tmax 20469 20465 0 11:24 ? 00:00:00 postgres: walwriter
tmax 20470 20465 0 11:24 ? 00:00:00 postgres: autovacuum launcher
tmax 20471 20465 0 11:24 ? 00:00:00 postgres: archiver last was 00000001000000000000001E
tmax 20472 20465 0 11:24 ? 00:00:00 postgres: stats collector
tmax 20473 20465 0 11:24 ? 00:00:00 postgres: logical replication launcher
tmax 20672 19606 0 11:33 pts/1 00:00:00 grep –color=auto postgres
- archiver last was 00000001000000000000001E
→ primary서버의 archiver 프로세스가 standby 서버로 WAL 파일을 전송하였습니다.
Standby 서버
[tmax@JY2C4G02:data]$ ps -ef | grep postgres
tmax 27019 1 0 11:26 pts/0 00:00:00 /usr/local/pgsql/bin/postgres
tmax 27020 27019 0 11:26 ? 00:00:00 postgres: startup waiting for 000000010000000000000020
tmax 27022 27019 0 11:26 ? 00:00:00 postgres: checkpointer
tmax 27023 27019 0 11:26 ? 00:00:00 postgres: background writer
tmax 27024 27019 0 11:26 ? 00:00:00 postgres: stats collector
tmax 27425 26449 0 11:37 pts/0 00:00:00 grep –color=auto postgres
- postgres: startup waiting for 000000010000000000000020
→ startup process가 restore을 위한 WAL 파일을 기다리고 있습니다.
Streaming Replication
Streaming Replication의 특징
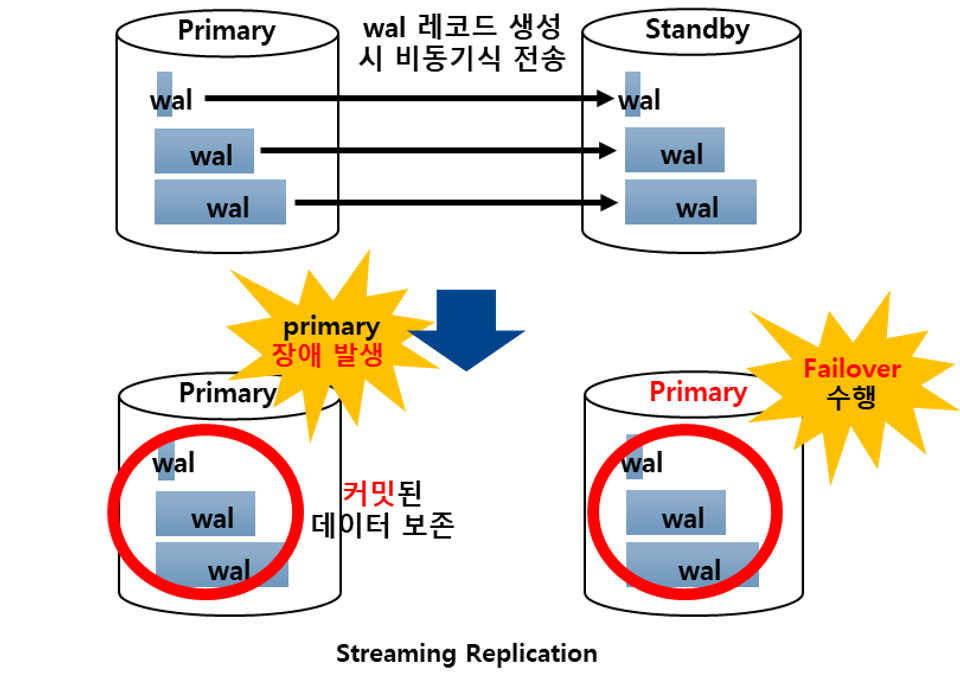
- WAL Record가 생성되면 즉시 Standby서버로 보내기 때문에 Log shipping Replication보다 Standby 서버를 최신 상태로 유지할 수 있습니다.
- Standby 서버를 Hot Standby로 운영하기 때문에 SELECT 조회가 가능합니다.
Streaming Replication 구축 방법
PostgreSQL v12 이전 버전
[Primary 서버]
1. Replication 전용 유저를 생성합니다.
CREATE USER [DBUSER] WITH REPLICATION PASSWORD '[PASSWORD]' LOGIN;
2. postgresql.conf 파일을 수정합니다.
`wal_level = replica
max_wal_sender=2
max_replication_slots=2`
3. replication slot을 생성합니다.
SELECT * FROM pg_create_physical_replication_slot('[REPLICATION SLOT]');
4. pg_hba.conf를 설정합니다.
host replication [DBUSER] [STANDBY IP] trust
- [DBUSER] : 새로 생성한 Replication 전용 유저
[Standby 서버]
1. pg_basebackup을 이용한 백업을 합니다.
pg_basebackup -h [primary IP] -p 5432 -U repluser -D /hypersql/pg/14/data -P -v -X stream
2. recovery.conf를 postgresql.conf 파일과 같은 위치에 생성합니다.
standby_mode=on primary_conninfo='host=[HOST IP] port=5432 user=[DBUSER] PASSWORD='PASSWORD'' primary_slot_name='[REPLICATION SLOT]'
PostgreSQL v12 ~
[Primary 서버]
1. Replication 전용 유저를 생성합니다.
CREATE USER [DBUSER] WITH REPLICATION PASSWORD '[PASSWORD]' LOGIN;
2. postgresql.conf 파일을 수정합니다.
cat << EOF >> $PGDATA/postgresql.conf max_wal_senders = 10 #defalt = 10 wal_level = replica max_replication_slots=3 EOF
max_wal_senders: 스트리밍 기반의 백업 클라이언트로부터 동시 연결 최대 수를 지정합니다. 항상 replication의 수보다 커야합니다.max_replication_slots: 서버가 지원할 수 있는 replication 슬롯의 최대 수를 지정합니다.wal_level: WAL 아카이빙 및 streaming replication을 하려면 replica 이상을 사용해야합니다.
3. replication slot을 생성합니다.
SELECT * FROM pg_create_physical_replication_slot('[REPLICATION SLOT]');
4. pg_hba.conf를 설정합니다.
host replication [DBUSER] [STANDBY IP] trust
- [DBUSER] : 새로 생성한 Replication 전용 유저
[Standby 서버]
1. pg_basebackup을 이용한 백업을 합니다.
pg_basebackup -h [primary IP] -p 5432 -U repluser -D /hypersql/pg/14/data -P -v -X stream
2. 데이터 디렉토리에서 myrecovery.conf 파일을 생성 후 primary server 정보를 입력합니다.
touch $PGDATA/myrecovery.conf
cat << EOF >> $PGDATA/myrecovery.conf
primary_conninfo=‘host=[primaryIP] port=5432 user=[DBUSER] password=[PASSWORD]’
primary_slot_name=‘[REPLICATION SLOT]’
EOF
- primary server 정보를 쉽게 보기 위해 파일을 따로 빼서 참조하는 것이기 때문에 파일명은 어떤 것이든 상관없습니다.
postgreSQL 12버전 이후부터는 이전 버전에서 사용하던 것 처럼 recovery.conf 파일을 생성할 경우 서버가 실행이 되지 않으므로 이름을 주의하여 생성하여야 합니다.
3. postgresql.conf 파일에 myrecovery.conf 파일을 참조하도록 설정합니다.
cat << EOF >> $PGDATA/postgresql.conf include_if_exists = '/hypersql/pg/14/data/myrecovery.conf' EOF
4. 데이터 디렉토리에 standby.signal 을 생성합니다.
cd $PGDATA touch standby.signal
5. 서버를 시작합니다.
pg_ctl start
동작 확인
[Primary 서버]
postgres=# select * from pg_stat_replication;
-[ RECORD 1 ]—-+——————————
pid | 59791
usesysid | 16384
usename | repluser
application_name | 192.168.40.137
client_addr | 192.168.40.137
client_hostname |
client_port | 37168
backend_start | 2022-08-30 06:14:12.754584-07
backend_xmin |
state | streaming
sent_lsn | 0/53000060
write_lsn | 0/53000060
flush_lsn | 0/53000060
replay_lsn | 0/53000060
write_lag |
flush_lag |
replay_lag |
sync_priority | 0
sync_state | async
reply_time | 2022-08-30 06:16:06.420532-07
[hypersql@localhost:pg_log]$ ps -ef | grep postgres
hypersql 57413 1 0 05:47 ? 00:00:00 /usr/pgsql-14/bin/postgres -D /hypersql/pg/14/data
hypersql 57414 57413 0 05:47 ? 00:00:00 postgres: logger
hypersql 57416 57413 0 05:47 ? 00:00:00 postgres: checkpointer
hypersql 57417 57413 0 05:47 ? 00:00:00 postgres: background writer
hypersql 57418 57413 0 05:47 ? 00:00:00 postgres: walwriter
hypersql 57419 57413 0 05:47 ? 00:00:00 postgres: autovacuum launcher
hypersql 57420 57413 0 05:47 ? 00:00:00 postgres: archiver last was 000000090000000000000052.00000028.backup
hypersql 57421 57413 0 05:47 ? 00:00:00 postgres: stats collector
hypersql 57422 57413 0 05:47 ? 00:00:00 postgres: logical replication launcher
hypersql 59791 57413 0 06:14 ? 00:00:00 postgres: walsender repluser 192.168.40.137(37168) streaming 0/53000060
hypersql 59896 49621 0 06:16 pts/1 00:00:00 grep –color=auto postgres
- archiver last was 000000090000000000000052.00000028.backup
→ archiver 프로세스가 WAL segment를 전송하였습니다. - walsender repluser 192.168.40.137(37168) streaming 0/53000060
→ WAL Record를 WAL sender 프로세스가 standby 데이터베이스로 보내는 중입니다.
[Standby 서버]
postgres=# SELECT * FROM pg_stat_wal_receiver; -[ RECORD 1 ]-
————————— pid | 51062 status | streaming receive_start_
lsn | 0/53000000 receive_start_tli | 9 written_lsn | 0/53000060 flushed_lsn |
0/53000060 received_tli | 9 last_msg_send_time | 2022-08-30 06:14:47.8473
74-07 last_msg_receipt_time | 2022-08-30 06:14:26.152722-07 latest_end_lsn
| 0/53000060 latest_end_time | 2022-08-30 06:14:17.789847-07 slot_name | 19
2_168_40_137 sender_host | 192.168.40.142 sender_port | 5432 conninfo | user=
repluser passfile=/hypersql/.pgpass channel_binding=prefer dbname=replication hos
t=192.168.40.142 port=5432 application_name=192.168.40.137 fallback_application
_name=walreceiver sslmode=prefer sslcompression=0 sslsni=1 ssl_min_protocol_versi
on=TLSv1.2 gssencmode=prefer krbsrvname=postgres target_session_attrs=any
[hypersql@localhost:pg_log]$ ps -ef | grep postgres
hypersql 51041 1 0 06:13 ? 00:00:00 /usr/pgsql-14/bin/postgres -D /hypersql/pg/14/data
hypersql 51042 51041 0 06:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: logger
hypersql 51043 51041 0 06:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: startup recovering 000000090000000000000053
hypersql 51050 51041 0 06:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: checkpointer
hypersql 51052 51041 0 06:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: background writer
hypersql 51053 51041 0 06:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: stats collector
hypersql 51062 51041 0 06:13 ? 00:00:00 postgres: walreceiver streaming 0/53000060
hypersql 51142 46734 0 06:15 pts/2 00:00:00 grep –color=auto postgres
- startup recovering 000000090000000000000053 → startup 프로세스가 WAL segment를 받지 못하여 기다리고 있는 상태입니다.
- walreceiver streaming 0/53000060 → WAL Record를 WAL receiver가 받아 streaming 중입니다.
Logical Replication
replication ID (보통 Primary key)를 기반으로 테이블 단위로 데이터 오브젝트와 변경사항을 복제하는 방식
Logical Replication의 특징
- Primary/Standby가 아닌 Publish/Subscribe의 개념으로 동기화 시킵니다.
- 테이블의 logical replication은 publish 데이터베이스에 있는 데이터의 스냅샷을 만들어 subscribe 데이터베이스에 복제합니다.
- 완료되면 publisher의 변경사항이 실시간으로 subscriber에게 전송됩니다.
Logical Replication 구축 방법
publish node
1. postgresql.conf 파일을 수정합니다.
wal_level = logical max_replication_slots=10 max_wal_senders=10
2. pg_hba.conf 파일을 설정합니다.
복제를 허용하도록 설정해야 합니다.
host replication [DBUSER] [SUBSCRIBER IP] trust
3. publication을 생성합니다.
CREATE PUBLICATION name
[ FOR TABLE [ ONLY ] table_name [ * ] [, …]
| FOR ALL TABLES ]
[ WITH ( publication_parameter [= value] [, … ] ) ]
- publication_parameter의 값은 insert, update, delete, truncate 중에 선택하여 입력 가능
- default는 ‘insert, update, delete, truncate’
subscribe node
1. postgresql.conf 파일을 수정합니다.
max_replication_slots =10
max_logical_replication_workers = 4
max_worker_processes = 8`
2. subscription을 생성합니다.
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION [SUBSCRIPTION NAME]
CONNECTION ‘dbname=[DBNAME] host=[PUBLISHER IP] user=[DBUSER]’ PUBLICATION;
Logical Replication 구축 실습
publish node
1. postgresql.conf 옵션을 설정하기
logical replication을 하기 위해 wal_level 파라미터 값을 수정합니다.
wal_level = logical
postgres=# SHOW wal_level;
wal_level
—————————
logical
(1 row)
2. pg_hba.conf 설정을 합니다.
subscribe node에서 접속할 수 있게 pg_hba.conf 파일을 수정합니다.host replication tmax 172.27.0.54/32 trust
3. 테이블 만들고 데이터를 입력합니다.
postgres=# CREATE TABLE test01(x int primary key, y int);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# INSERT INTO test01 VALUES(13,24);
INSERT 0 1postgres=# SELECT * FROM test01;
x | y
—-+—-
13 | 24
(1 row)
4. publication을 만듭니다.
postgres=# CREATE PUBLICATION my_publication FOR TABLE test01; CREATE PUBLICATION
subscribe node
1. 테이블을 만듭니다.
postgres=# CREATE TABLE test01(x int primary key, y int);
CREATE TABLE
2. subscription 만들기
postgres=# CREATE SUBSCRIPTION my_subscription CONNECTION ‘host=211.253.38.213 port=5432 dbname=postgres’ PUBLICATION my_publication;
NOTICE: created replication slot “my_subscription” on publisher
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION
postgres=# 2022-04-28 19:19:03.788 KST [7340] LOG: logical replication apply worker for subscription “my_subscription” has started
2022-04-28 19:19:03.795 KST [7341] LOG: logical replication table synchronization worker for subscription “my_subscription”, table “test01” has started
2022-04-28 19:19:03.814 KST [7341] LOG: logical replication table synchronization worker for subscription “my_subscription”, table “test01” has finished
3. 복제되었는지 확인하기
postgres=# SELECT * FROM test01;
x | y
—-+—-
13 | 24
(1 row)
확인
변경사항이 복제되는지 확인해보는 작업을 합니다.
publish node에서 새로운 데이터 입력
postgres=# INSERT INTO test01 VALUES(30,20);
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# SELECT * FROM test01;
x | y
—-+—-
13 | 24
30 | 20
(2 rows)
subscribe node에서 테이블 확인
postgres=# SELECT * FROM test01;
x | y
—-+—-
13 | 24
30 | 20
(2 rows)
Synchronous Replication
Synchronous Replication의 특징
PostgreSQL Streaming Replication은 기본적으로 비동기식(Asynchronous)입니다. Primary 서버가 장애로 멈춰, Standby서버가 Primary서버로 Failover 될 때 동기화에 지연이 있었다면 그만큼 데이터를 손실되게 됩니다.
이러한 복제방식을 사용하면 Primary 및 Standby 서버가 모두 WAL파일에 쓰여졌을 때 정상적으로 처리되었다고 판단합니다. 그러면 Standby 서버에서 자료손실이 일어나지 않게 됩니다. 이렇게 되면 안정성이 보장되지만 상대적으로 비용이 증가하게 됩니다. 다음 트랜잭션은 현재 트랜잭션이 Standby 서버로부터 응답을 받아야만 작업이 진행되기 때문에 지연이 생길 수 밖에 없습니다.
Read-only 트랜잭션과 트랜잭션 rollback의 경우에는 standby서버로 부터 응답을 기다리지 않습니다. 그리고 Subtransaction commit의 경우에는 응답을 기다리지 않고 top-level commit의 경우에만 기다립니다. 또한 데이터 로드 및 인덱스 작성과 같은 긴 작업들에 대한 최종 commit 메세지를 기다리지 않습니다. 하지만 2PC(이중 커밋)에 대한 모든 작업은 기다립니다.
Synchronous Replication의 구축 방법
먼저 Streaming Replication을 구성합니다. (Streaming Replication 구축 방법 참고)
Primary 서버 구성
- Primary 서버에 postgresql.conf에
synchronous_standby_names의 값을 비어있지 않게 설정합니다. synchronous_commit의 값을on으로 설정해야하지만 기본값이on으로 설정되어 있어 일반적으로는 변경하지 않아도 됩니다.
synchronous_standby_names = ‘s1’#synchronous_commit = on
Standby 서버 구성
Primary에서 설정해주는 synchrouns_standby_names 는 각 standby 서버에 있는 primary_conninfo의 application_name 입니다. 12버전 이상은 postgresql.conf , 그 이하는 recovery.conf 에 해당 정보를 기입합니다.
primary_conninfo = ‘host=localhost port=5432 user=postgres application_name=”s1”’
Commit 레코드가 Primary 서버의 WAL 세그먼트 파일에 기록된 후에, 그 레코드를 Standby 서버로 보냅니다. Standby 서버는 그것을 자신의 WAL 세그먼트 파일에 기록한 뒤에 wal_receiver_status_interval 의 값이 0으로 지정되어 있지 않으면, Primary 서버에 즉시 완료되었다고 응답을 보냅니다. 이 복제 방식은 직접 연결된 Standby 서버만 가능하고 Standby 서버의 하위 서버들에 대해서는 동기식 복제 방식을 사용할 수 없습니다.
synchronous_commit 설정값을 remote_write 로 설정하게 되면, OS 차원에서 디스크에 기록되었다는 것까지만 확인합니다. 실제로 OS가 Disk Buffer의 내용을 물리적으로 Disk에 기록했다는 것을 확인하지 않습니다.
다중 Synchronous Standby
Synchronous Standby는 다중 Standby를 지원합니다. 모든 Standby 서버가 데이터를 수신할 때까지 기다립니다. synchronous_standby_names 에 기입된 서버들의 수만큼 응답을 기다립니다. FIRST , ANY 라는 메소드를 이용하여 파라미터를 설정할 수 있습니다.
- 우선순위 기반 동기 복제 (
FIRST) s1,s2,s3,s4 총 4대의 Standby 서버가 구성되어 있어 있습니다.FIRST 2로 s1,s2가 동기로 선택되었으며 s3는 잠재적으로 s1,s2의 동기가 실패했을 경우에 선택되는 서버로 지정되었습니다. s4의 경우에는 작성되어 있지 않기 때문에 비동기식으로 동작합니다.
synchronous_standby_names = ‘FIRST 2 (s1, s2, s3)’
- 쿼럼 기반 동기 복제 (ANY) s1,s2,s3,s4 총 4대의 Standby 서버가 구성되어 있어 있습니다. ANY 2 는 현재 기입된 서버들 중 적어도 2개의 서버에서 응답을 받을 때까지 기다립니다.
synchronous_standby_names = ‘ANY 2 (s1, s2, s3)’
sync_state는 pg_stat_replication 뷰에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
select * from pg_catalog.pg_stat_replication;
postgres=# select pid, client_addr, application_name, state, sync_priority, sync_state from pg_catalog.pg_stat_replication;
pid | client_addr | application_name | state | sync_priority | sync_state
——-+————-+——————+———–+—————+————
23745 | 172.27.1.43 | s3 | streaming | 3 | potential
23695 | 172.27.0.68 | s1 | streaming | 1 | sync
23757 | 172.27.0.68 | s2 | streaming | 2 | sync
(3 rows)
성능 테스트
scale=100 기준 테스트
- Primary Node 만
-bash-4.2$ pgbench -c 50 -j 4 -t 1000
starting vacuum…end.
transaction type:
scaling factor: 100
query mode: simple
number of clients: 50
number of threads: 4
number of transactions per client: 1000
number of transactions actually processed: 50000/50000
latency average = 12.491 ms
tps = 4002.948744 (including connections establishing)
tps = 4003.897213 (excluding connections establishing)
- Standby Node 1개를 Synchronous로 연결
bash-4.2$ pgbench -c 50 -j 4 -t 1000
starting vacuum…end.
transaction type: <builtin: TPC-B (sort of)>
scaling factor: 100
query mode: simple
number of clients: 50
number of threads: 4
number of transactions per client: 1000
number of transactions actually processed: 50000/50000
latency average = 36.005 ms
tps = 1388.677665 (including connections establishing)
tps = 1388.793393 (excluding connections establishing)
지금까지 ‘PostgreSQL의 Replication’에 관해 알아보았습니다
‘PostgreSQL의 (Interface) C lang – libpq’를 바로 이어서 확인해보세요!
